Serengeti National Park
Serengeti National Park
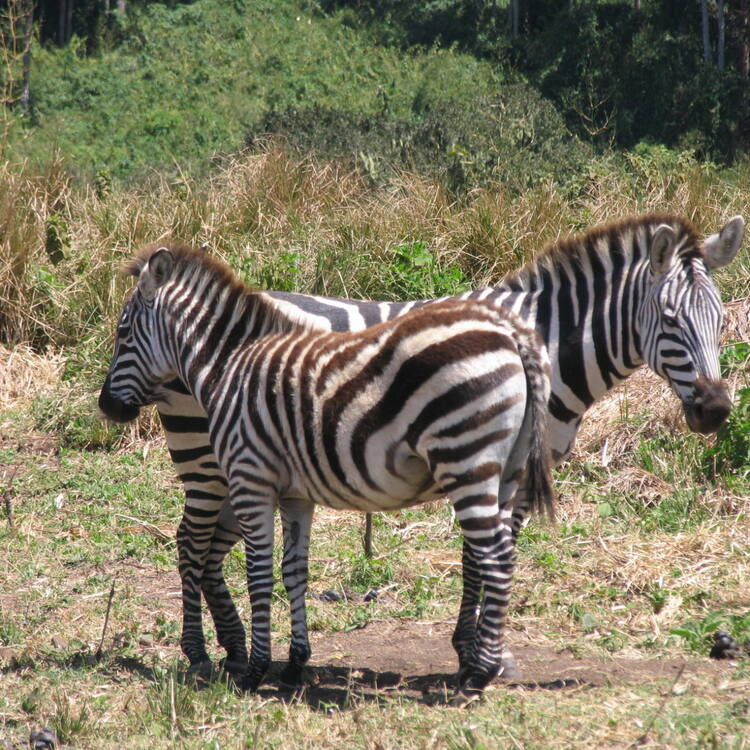
The vast plains of the Serengeti comprise 1.5 million ha of savannah. The annual migration to permanent water holes of vast herds of herbivores (wildebeest, gazelles and zebras), followed by their predators, is one of the most impressive natural events in the world.
Description is available under license CC-BY-SA IGO 3.0
Parc national de Serengeti
Dans les vastes plaines de Serengeti, sur un million et demi d'hectares de savanes, les migrations annuelles vers les points d'eau permanents d'immenses troupeaux de millions d'herbivores – gnous, gazelles, zèbres – suivis de leurs prédateurs, offrent un spectacle d'un autre âge, l'un des plus impressionnants au monde.
Description is available under license CC-BY-SA IGO 3.0
روضة سيرنقيطي الوطنية
يمكن التمتع في سهول سيرنقيطي الشاسعة وعلى امتداد مليون هكتار ونصف من السهب (سافانا) بمنظر من عصر آخر يعتبر من أروع المشاهد في العالم ويتمثل في الهجرة السنوية لقطعان من ملايين الحيوانات الآكلة للأعشاب كظبي النو والغزلان وحمار الزرد، يتبعها مفترسوها الى نقاط مياه لا تنضب.
source: UNESCO/CPE
Description is available under license CC-BY-SA IGO 3.0
塞伦盖蒂国家公园
在广袤的塞伦盖蒂平原上有150万公顷的大草原和数量众多的食草动物羚羊、瞪羚和斑马。每年,当它们为寻找水源而迁徙时,总有食肉动物尾随其后,这是世界上最壮观的景象之一。
source: UNESCO/CPE
Description is available under license CC-BY-SA IGO 3.0
Национальный парк Серенгети
Безбрежные равнинные саванны этого парка занимают площадь 1,5 млн. га. Круглогодичная непрекращающаяся миграция сопровождаемых хищниками крупных стад копытных (антилопы гну, газели, зебры), которые ищут водопой, считается одним из самых ярких сезонных явлений в дикой природе.
source: UNESCO/CPE
Description is available under license CC-BY-SA IGO 3.0
Parque Nacional de Serengeti
En este parque de un millón y medio de hectáreas de vastas llanuras de sabana, las inmensas manadas de millones de herbívoros –ñus, gacelas y cebras– y los predadores que les siguen en sus migraciones anuales en busca de abrevaderos estables, ofrecen uno de los más impresionantes espectáculos del mundo de la naturaleza.
source: UNESCO/CPE
Description is available under license CC-BY-SA IGO 3.0
セレンゲティ国立公園
ヴィクトリア湖東の3州にまたがるタンザニア最大の国立公園。アフリカのサバンナ地帯の中心にあり、東アフリカの300万頭以上の野生動物の楽園、避難所となっている。1957年以来のドイツ人グルメジック父子の国立公園拡大の努力と、タンザニア政府の優れた自然環境保護政策のもとで、野生動物の複雑な生態系の観察・研究の地球上に比類の無い実験室となっている。source: NFUAJ
Nationaal park Serengeti
De Serengeti-vlakte beslaat 1,5 miljoen hectare savanne en herbergt de grootste migratie van dieren ter wereld. Zo'n twee miljoen gnoes en honderdduizenden andere hoefdieren (gazellen en zebra’s) doen mee aan een jaarlijkse cirkelvormige trektocht door Kenia en Tanzania op zoek naar grasland en water. De enorme massa herbivoren wordt gevolgd door roofdieren wat een zeer indrukwekkend, natuurlijk spektakel oplevert. De biologische diversiteit van het park is zeer hoog. Er leven ten minste vier bedreigde of uitstervende diersoorten: de zwarte neushoorn, de olifant, wilde honden en cheeta’s.
Source: unesco.nl
Outstanding Universal Value
Brief synthesis
In the vast plains of Serengeti National Park, comprising 1.5 million hectares of savannah, the annual migration of two million wildebeests plus hundreds of thousands of gazelles and zebras - followed by their predators in their annual migration in search of pasture and water – is one of the most impressive nature spectacles in the world. The biological diversity of the park is very high with at least four globally threatened or endangered animal species: black rhinoceros, elephant, wild dog, and cheetah.
Criterion (vii): The Serengeti plains harbour the largest remaining unaltered animal migration in the world where over one million wildebeest plus hundreds of thousands of other ungulates engage in a 1,000 km long annual circular trek spanning the two adjacent countries of Kenya and Tanzania. This spectacular phenomenon takes place in a unique scenic setting of ‘endless plains’: 25,000km2 of treeless expanses of spectacularly flat short grasslands dotted with rocky outcrops (kopjes) interspersed with rivers and woodlands. The Park also hosts one of the largest and most diverse large predator-prey interactions worldwide, providing a particularly impressive aesthetic experience.
Criterion (x): The remarkable spatial-temporal gradient in abiotic factors such as rainfall, temperature, topography and geology, soils and drainage systems in Serengeti National Park manifests in a wide variety of aquatic and terrestrial habitats. The combination of volcanic soils combined with the ecological impact of the migration results in one of the most productive ecosystems on earth, sustaining the largest number of ungulates and the highest concentration of large predators in the world. The ecosystem supports 2 million wildebeests, 900,000 Thomson’s gazelles and 300,000 zebras as the dominant herds. Other herbivores include 7,000 elands, 27,000 topis, 18,000 hartebeests, 70,000 buffalos, 4,000 giraffes, 15,000 warthogs, 3,000 waterbucks, 2,700 elephants, 500 hippopotamuses, 200 black rhinoceroses, 10 species of antelope and 10 species of primate. Major predators include 4,000 lions, 1000 leopards, 225 cheetahs, 3,500 spotted hyenas and 300 wild dogs. Of these, the black rhino Diceros bicornis, leopard Panthera pardus, African elephant Loxodonta africana and cheetah Acynonix jubatus are listed in the IUCN Red List. There are over 500 species of birds that are perennially or seasonally present in the Park, of which five species are endemic to Tanzania. The Park has the highest ostrich population in Tanzania and probably Africa, making the population globally important.
Integrity
Serengeti National Park is at the heart the larger Serengeti ecosystem, which is defined by the area covered by the annual migration. The property is contiguous with Ngorongoro Conservation Unit, an area of 528,000ha declared a World Heritage Site in 1979. The entire ecosystem also includes the Maswa Game Reserve (2,200km2) in the south, Grumeti and Ikorongo Game Reserves in the east, Maasai Mara National Reserve in Kenya (1,672km2) to the north, and Loliondo Game Controlled Area in the west. This entire ecosystem is intact and no barriers hamper the migration. Serengeti National Park is sufficiently large and intact to ensure the survival and vigour of all the species contained therein, if maintained in its present state but does not, by itself, ensure the protection of the entire ecosystem. However, all other parts of the ecosystem do have a greater or lesser degree of protection. A potential threat is the plan to build a transport infrastructure through the Serengeti. This would essentially cut the ecosystem into two halves, with predictably negative consequences on the Serengeti. Adding Maswa Game Reserve and Maasai Mara National Reserve to the World Heritage List, or giving then the status of a buffer zone would further safeguard the Outstanding Universal Values of this property.
Another major potential threat to the integrity of the Park is the scarcity of surface water for the animals during dry years, as only one river (Mara) flows perennially through the Park. An extension of the Park boundary to reach Lake Victoria providing a corridor for animals to access water in times of drought is planned for the future to address this issue.
Protection and management requirements
The site has a well designated and partially demarcated boundary, and since 2009 funds have been allocated to demarcate the entire boundary. Its management is regulated by both international and government policies and legal obligations. The National Parks Ordinance Cap 412 of 1959 provides for Tanzania National Parks with the mandate to manage the site. In addition, The 1974 Tanzanian Wildlife Conservation Act and the 2009 Wildlife Conservation Act provide for both within the site and adjacent area protection of resources, respectively. A General Management Plan (2006-2016) has been formulated to guide the daily management of the site in a sustainable manner and is currently being implemented. The Plan provides guidance on how to execute the various activities within the park under four main Themes: Ecosystem Management, Outreach services, Tourism Management and Park Operations. The site has a reasonable level of human and financial resources for effective management, but as the activities expand, and more challenges emerge, the lack of sufficient resources remains a potential future constraint. The major management concerns include poaching, tourism pressure, wildfires, and lack of adequate capacity in resource monitoring. Another important management challenge is water: despite numerous sources of water during the rain season, there is only one perennial river (Mara) which is transnational. However, this river currently faces multiple human-mediated cross-boundary threats.
Links
-
Google Arts & Culture: Story
-
Tanzania National Parks' Twitter page
-
Tanzania National Parks' YouTube account
-
Serengeti National Park's Instagram page
-
Tanzania National Park's Instagram page
-
Serengeti National Park's Facebook page
-
Serengeti National Park's official website page
-
 View photos from OUR PLACE the World Heritage collection
View photos from OUR PLACE the World Heritage collection
-
Tanzania Tourism Board
-
Protectedplanet.net