Qatar and Fiji get their first World Heritage sites as World Heritage Committee makes six additions to UNESCO List
Qatar and Fiji had their first World Heritage sites inscribed during the afternoon session of the World Heritage Committee on Saturday, as the intergovernmental body added six properties to UNESCO’s World Heritage List
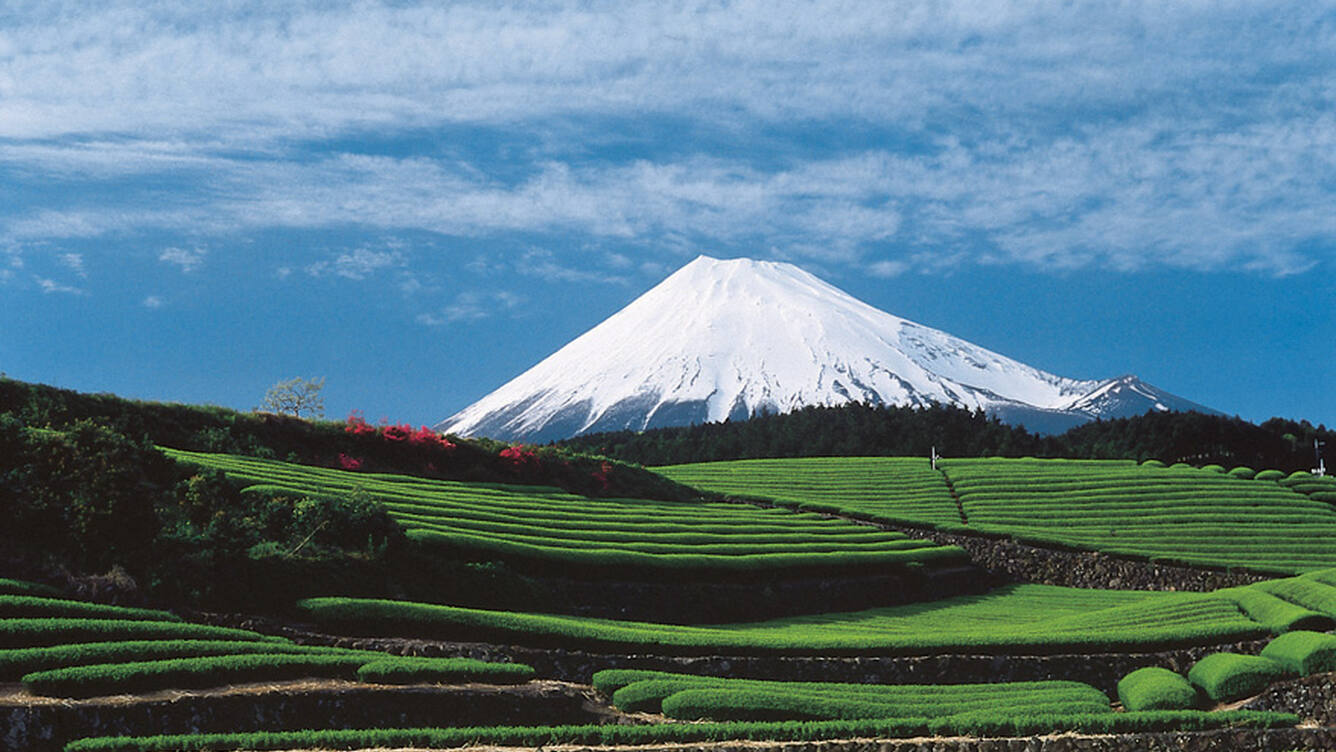
Fujisan, Sacred Place and Source of Artistic Inspiration (Japan)
The beauty of the solitary, often snow-capped, stratovolcano, known around the world as Mount Fuji, rising above villages and tree-fringed sea and lakes has long inspired artists and poets and been the object of pilgrimages. Its representation in Japanese art goes back to the 11th century but 19th century wood block prints have made Fujisan become an internationally recognized icon of Japan and have had a deep impact on the development of Western art. The inscribed property consists of 25 sites which reflect the essence of Fujisan’s sacred landscape. In the 12th century, Fujisan became the centre of training for ascetic Buddhism, which included Shinto elements. On the upper 1,500-metre tier of the 3,776m mountain, pilgrim routes and crater shrines have been inscribed alongside sites around the base of the mountain including Sengen-jinja shrines, Oshi lodging houses, and natural volcanic features such as lava tree moulds, lakes, springs and waterfalls, which are revered as sacred.
University of Coimbra—Alta and Sofia (Portugal)
Situated on a hill overlooking the city, the University of Coimbra with its colleges grew and evolved over more than seven centuries within the old town. Notable university buildings include the 12th century Cathedral of Santa Cruz and a number of 16th century colleges, the Royal Palace of Alcáçova, which has housed the University since 1537, the Joanine Library with its rich baroque decor, the 18th century Botanical Garden and University Press, as well as the large “University City” created during the 1940s. The University’s edifices became a reference in the development of other institutions of higher education in the Portuguese-speaking world where it also exerted a major influence on learning and literature. Coimbra offers an outstanding example of an integrated university city with a specific urban typology as well as its own ceremonial and cultural traditions that have been kept alive through the ages.
Historic Centre of Agadez (Niger)
Known as the gateway to the desert, Agadez, on the southern edge of the Sahara desert, developed in the 15th and 16th centuries when the Sultanate of Aïr was established and Touareg tribes were sedentarized in the city, respecting the boundaries of old encampments, which gave rise to a street pattern still in place today. The historic centre of the city, an important crossroads of the caravan trade, is divided into 11 quarters with irregular shapes. They contains numerous earthen dwellings and a well-preserved group of palatial and religious buildings including a 27m high minaret made entirely of mud brick, the highest such structure in the world. The site is marked by ancestral cultural, commercial and handicraft traditions still practiced today and presents exceptional and sophisticated examples of earthen architecture.
Al Zubarah Archaeological Site (Qatar)
The walled coastal town of Al Zubarah in the Gulf flourished as a pearling and trading centre in the late 18th century and early 19th centuries, before it was destroyed in 1811 and abandoned in the early 1900s. Founded by merchants from Kuwait, Al Zubarah had trading links across the Indian Ocean, Arabia and Western Asia. A layer of sand blown from the desert has protected the remains of the site’s palaces, mosques, streets, courtyard houses, and fishermen’s huts; its harbour and double defensive walls, a canal, walls, and cemeteries. Excavation has only taken place over a small part of the site, which offers an outstanding testimony to an urban trading and pearl-diving tradition which sustained the region’s major coastal towns and led to the development of small independent states that flourished outside the control of the Ottoman, European, and Persian empires and eventually led to the emergence of modern day Gulf States.
Levuka Historical Port Town (Fiji)
The town and its low line of buildings set among coconut and mango trees along the beach front was the first colonial capital of Fiji, ceded to the British in 1874. It developed from the early 19th century as a centre of commercial activity by Americans and Europeans who built warehouses, stores, port facilities, residences, and religious, educational and social institutions around the villages of the South Pacific island’s indigenous population. It is a rare example of a late colonial port town that was influenced in its development by the indigenous community which continued to outnumber the European settlers. Thus the town, an outstanding example of late 19th century Pacific port settlements, reflects the integration of local building traditions by a supreme naval power, leading to the emergence of a unique landscape.
Red Bay Basque Whaling Station (Canada)
Red Bay, established by Basque mariners in the 16th century at the north-eastern tip of Canada on the shore of the Strait of Belle Isle is an archaeological site that provides the earliest, most complete and best preserved testimony of the European whaling tradition. Gran Baya, as it was called by those who founded the station in 1530s, was used as a base for coastal hunting, butchering, rendering of whale fat by heading to produce oil and storage. It became a major source of whale oil which was shipped to Europe where it was used for lighting. The site, which was used in the summer months, includes remains of rendering ovens, cooperages, wharves, temporary living quarters and a cemetery, together with underwater remains of vessels and whale bone deposits. The station was used for some 70 years, before the local whale population was depleted.
During its morning session on , the World Heritage Committee inscribed the Cultural Landscape of Honghe Hani Rice Terraces (China) and Lesotho’s Sehlabathebe National Park as an extension to the uKhahlamba Drakensberg Park (in South Africa), which is now to be named Maloti Drakensberg Tranboundary World Heritage Site.
Additions to the World Heritage List are to continue Sunday. The 37th session, taking place in Phnom Penh, will close in Angkor on 27 June.